Top 10 Malware March 2022
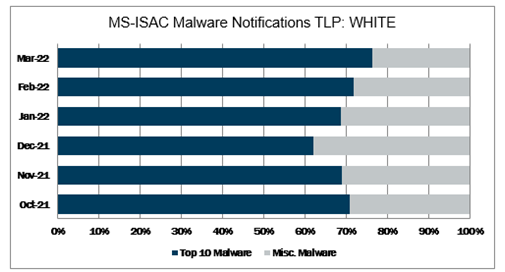
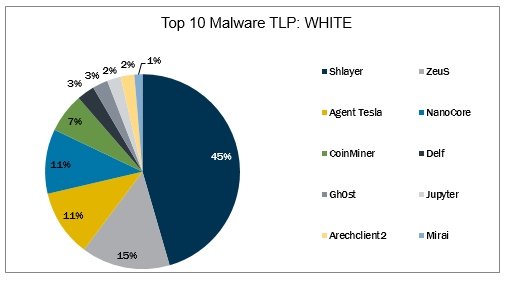
In March 2022, the Top 10 stayed consistent with the previous month with malware changing spots in the Top 10. This is with the exception of Gh0st and Jupyter, both returning to the Top 10. Gh0st is a RAT used to control infected endpoints. Gh0st is dropped by other malware to create a backdoor into a device that allows an attacker to fully control the infected device. Jupyter, aka SolarMarker, is a highly evasive and adaptive .NET infostealer that is downloaded by leveraging SEO-poisoning to create watering hole sites for the purpose of deceiving unsuspecting users who visit the website and download a malicious document, often a zip or PDF file embedded with a malicious executable. The Top 10 Malware variants comprise 76% of the total malware activity in March 2022, increasing 4% from February 2022.
Malware Infection Vectors
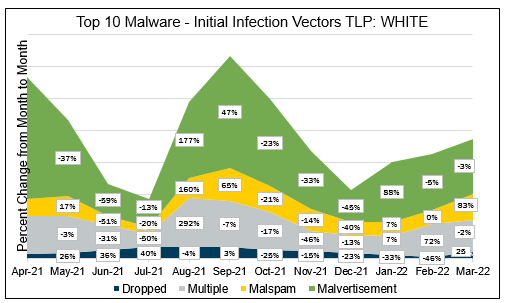
The MS-ISAC tracks potential primary infection vectors for our Top 10 Malware each month based on open-source reporting, as depicted in the graph below. We currently track four initial infection vectors: Dropped, Malvertisement, Malspam, and Network. The MS-ISAC has not had any malware in the Top 10 use the initial infection vector Network in the past year. Some malware employ different vectors in different contexts and are thus tracked as Multiple.
Our Community Defense Model (CDM) v2.0 can help you defend against 77% of ATT&CK (sub-)techniques associated with malware – regardless of the infection vector they use. Learn more in the video below.
In March 2022, Malvertisement accounted for the greatest number of alerts. Malvertisement remains the top initial infection vector due to Shlayer activity. Activity levels for Malvertisement, and Multiple decreased, while activity for Dropped and Malspam increased. It is likely that Malvertisement will remain the primary infection vector as the Shlayer campaign continues. The Multiple category increases and decreases at an unpredictable rate, which making it difficult to analyze trends. This category will likely continue to comprise a significant portion of the initial infection vectors as malware becomes more sophisticated and employs multiple methods to infect systems. Malspam consistently represents a portion of the Top 10 malware as it is one of the oldest and most reliable primary initial infection vectors used by cyber threat actors in both this category and the Multiple category.
Dropped – Malware delivered by other malware already on the system, an exploit kit, infected third-party software, or manually by a cyber threat actor. Currently, Gh0st, Jupyter, and Mirai are the malware using this technique.
Multiple – Malware that currently favors at least two vectors. Currently, Arechclient2, CoinMiner, Delf, and ZeuS are the malware utilizing multiple vectors.
Malspam – Unsolicited emails either direct users to malicious web sites or trick users into downloading or opening malware. Top 10 Malware using this technique include Agent Tesla and NanoCore.
Malvertisement – Malware introduced through malicious advertisements. Currently, Shlayer is the only Top 10 Malware using this technique.
Top 10 Malware and IOCs
Below are the Top 10 Malware ranked in order of prevalence. The respective indicators of compromise (IOCs) are provided to aid in detecting and preventing infections from these Top 10 Malware variants. Note: The associated URIs are aligned with malware’s respective domain(s) or IP(s) and increase the likelihood of maliciousness when found together. The URIs alone are not inherently malicious.
1. Shlayer
Shlayer is a downloader and dropper for MacOS malware. It is primarily distributed through malicious websites, hijacked domains, and malvertizing posing as a fake Adobe Flash updater.
All Shlayer domains follow the same pattern <api.random_name.com>. Below area several examples of domains Shlayer uses.</api.random_name.com>
Domains
- api[.]interfacecache[.]com
- api[.]scalableunit[.]com
- api[.]typicalconfig[.]com
- api[.]standartanalog[.]com
- api[.]fieldenumerator[.]com
- api[.]practicalsprint[.]com
- api[.]searchwebsvc[.]com
- api[.]connectedtask[.]com
- api[.]navigationbuffer[.]com
- api[.]windowtask[.]com
2. ZeuS
ZeuS is a modular banking trojan which uses keystroke logging to compromise victim credentials when the user visits a banking website. Since the release of the ZeuS source code in 2011, many other malware variants have adopted parts of its codebase, which means that events classified as ZeuS may actually be other malware using parts of the ZeuS code.
3. Agent Tesla
Agent Tesla is a RAT that exfiltrate credentials, log keystrokes, and capture screenshots from an infected computer.
4. NanoCore
NanoCore is a RAT spread via malspam as a malicious Excel XLS spreadsheet. As a RAT, NanoCore can accept commands to download and execute files, visit websites, and add registry keys for persistence.
5. CoinMiner
CoinMiner is a cryptocurrency miner family that typically uses Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and EternalBlue to spread across a network. Additionally, it typically uses the WMI Standard Event Consumer scripting to execute scripts for persistence. However, due to multiple variants of this malware, capabilities may vary. CoinMiner spreads through malspam or is dropped by other malware.
6. Delf
Delf is a family of malware with multiple variants written in the Delphi programming language, where most are downloaders. Campaigns, targets, infection vectors and capabilities vary based on the variant. Delf has multiple initial infection vectors, such as: dropped, malspam, or unintentional downloaded from a malicious website. Some of the abilities Delf variants exhibit include: backdoor or proxy functionality, stealing information, terminating antivirus applications, and mass mailing.
7. Gh0st
Gh0st is a RAT used to control infected endpoints. Gh0st is dropped by other malware to create a backdoor into a device that allows an attacker to fully control the infected device.
8. Jupyter
Jupyter aka SolarMarker, is a highly evasive and adaptive .NET infostealer that is downloaded by leveraging SEO-poisoning to create watering hole sites for the purpose of deceiving unsuspecting users to visit the website and download a malicious document, often a zip or PDF file embedded with a malicious executable. Jupyter primarily targets browser data in browsers such as Chrome, Chromium, and Firefox and has full backdoor functionality.
IPs
- 37[.]120.233[.]92
- 89[.]44.9[.]108
- 92[.]204.160[.]101
- 92[.]204.160[.]114
- 146[.]70.101[.]97
- 146[.]70.53[.]153
- 146[.]70.40[.]236
- 193[.]29.104[.]89
9. Arechclient2
Arechclient2, aka SectopRAT, is a .NET RAT with numerous capabilities including multiple stealth functions. Arechclient2 can profile victim systems, steal information such as browser and crypto-wallet data, and launch a hidden secondary desktop to control browser sessions. Additionally, it has several anti-VM and anti-emulator capabilities.
10. Mirai
Mirai is a malware botnet known to compromise Internet of Things (IoT) devices in order to conduct large-scale DDoS attacks. Mirai is dropped after an exploit has allowed the attacker to gain access to a machine.
As of June 23, 2025, the MS-ISAC has introduced a fee-based membership. Any potential reference to no-cost MS-ISAC services no longer applies.