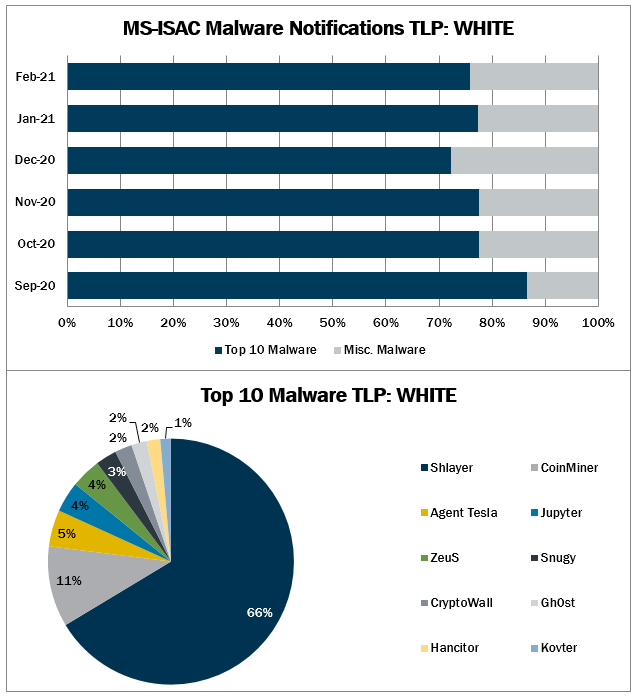
Top 10 Malware February 2021
In February 2021, malvertisement accounted for the greatest number of alerts. Malvertisement continues as the top initial infection vector due to Shlayer activity. Shlayer returned to the Top 10 Malware after new evidence resulted in it being reclassified as a trojan downloader compared to an adware dropper. Activity levels for dropped and multiple increased, while activity for malspam and malvertisement decreased. It is highly likely that malvertisement will remain the primary infection vector as the Shlayer campaign pans out.
Our Community Defense Model (CDM) v2.0 can help you defend against 77% of ATT&CK (sub-)techniques associated with malware – regardless of the infection vector they use. Learn more in the video below.
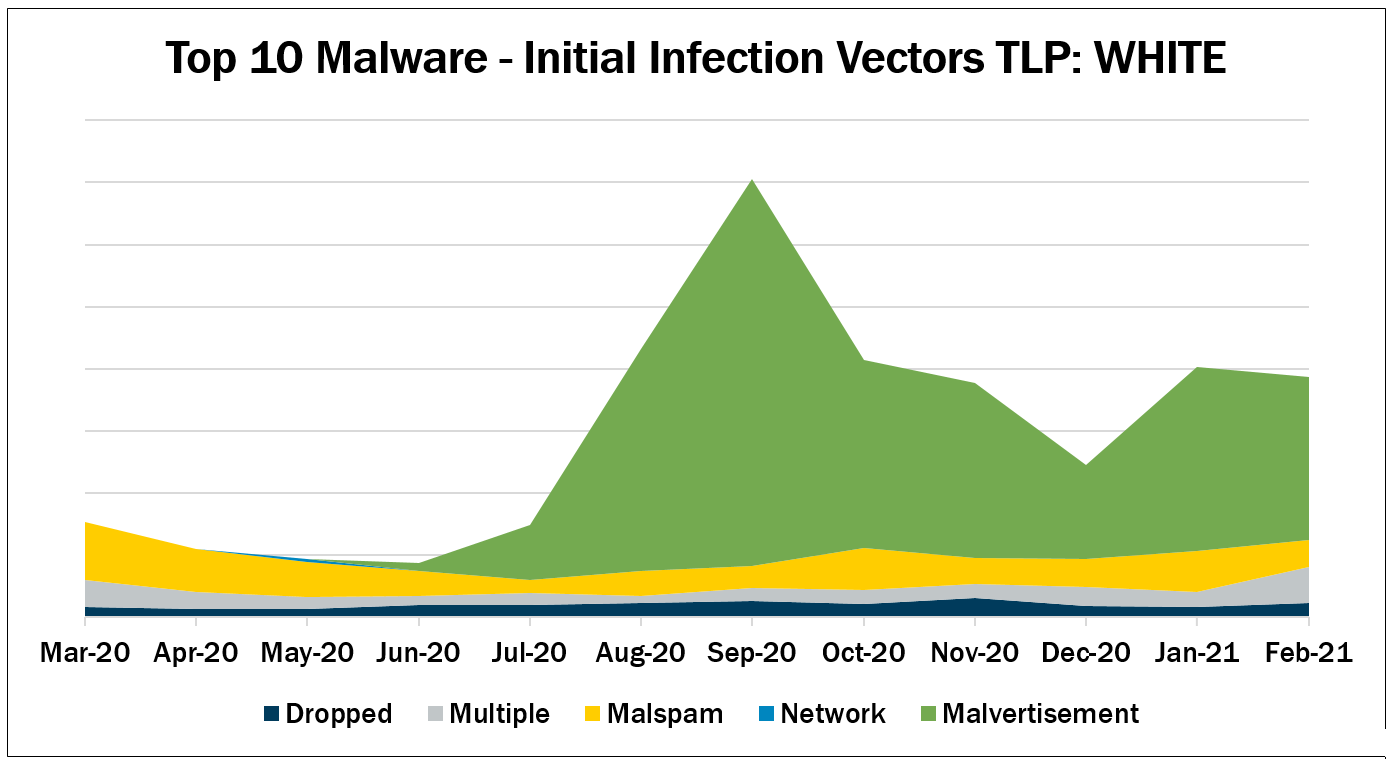
Dropped – Malware delivered by other malware already on the system, an exploit kit, infected third-party software, or manually by a cyber threat actor. Gh0st and Jupyter are the only malware dropped.
Multiple – Malware that favors at least two vectors. Currently, CoinMiner, CryptoWall, and ZeuS are the malware utilizing multiple vectors. ZeuS is dropped by other malware, but it is also delivered via malvertisement.
Malspam – Unsolicited emails, which either direct users to malicious web sites or trick users into downloading or opening malware. Top 10 Malware using this technique Agent Tesla, Hancitor, Kovter, and Snugy.
Malvertisement – Malware introduced through malicious advertisements. Currently, Shlayer is the only Top 10 Malware using this technique.
Top 10 Malware and IOCs
Below are the Top 10 Malware ranked in order of prevalence. The respective indicators of compromise (IOCs) are provided to aid in detecting and preventing infections from these Top 10 Malware variants. Note: The associated URIs are aligned with malware’s respective domain(s) or IP(s) and increase the likelihood of maliciousness when found together. The URIs alone are not inherently malicious.
1. Shlayer
Shlayer is a downloader and dropper for MacOS malware. It is primarily distributed through malicious websites, hijacked domains, and malvertizing posing as a fake Adobe Flash updater. All Shlayer domains follow the same pattern <api.random_name.com>. Below are several examples of domains Shlayer uses.</api.random_name.com>
Domains
- api[.]interfacecache[.]com
- api[.]scalableunit[.]com
- api[.]typicalconfig[.]com
- api[.]standartanalog[.]com
- api[.]fieldenumerator[.]com
- api[.]practicalsprint[.]com
- api[.]searchwebsvc[.]com
- api[.]connectedtask[.]com
- api[.]navigationbuffer[.]com
- api[.]windowtask[.]com
2. CoinMiner
CoinMiner is a cryptocurrency miner that uses Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and EternalBlue to spread across a network. CoinMiner uses the WMI Standard Event Consumer scripting to execute scripts for persistence. CoinMiner spreads through malspam or is dropped by other malware.
3. Agent Tesla
Agent Tesla is a RAT that exfiltrates credentials, logs keystrokes, and captures screenshots from an infected computer.
4. Jupyter
Jupyter is an infostealer downloaded by masquerading as legitimate software. Its primarily targets browser data in browsers such as Chrome, Chromium, and Firefox and has full backdoor functionality.
5. ZeuS
ZeuS is a modular banking trojan which uses keystroke logging to compromise victim credentials when the user visits a banking website. Since the release of the ZeuS source code in 2011, many other malware variants have adopted parts of its codebase, which means that events classified as ZeuS may actually be other malware using parts of the ZeuS code.
IP
- 176.121.14[.]151
URI
- /gate.php
6. Snugy
Snugy is a PowerShell-based backdoor allowing the attacker to obtain the system’s hostname and run commands. This backdoor communicates through a DNS tunneling channel on the compromised server.
7. CryptoWall
CryptoWall is a ransomware commonly distributed through malspam with malicious ZIP attachments, Java vulnerabilities, and malicious advertisements. Upon successful infection, CryptoWall will scan the system for drive letters, network shares, and removable drives. CryptoWall runs on both 32-bit and 64-bit systems.
8. Ghost
Gh0st is a RAT used to control infected endpoints. Gh0st is dropped by other malware to create a backdoor into a device that allows an attacker to fully control the infected device.
9. Hancitor
Hancitor, also known as Chanitor or Tordal, is a downloader that spreads through malspam containing malicious Microsoft Office documents, links, and attachments. This malware has been known to download additional malware, such as Pony, Ursnif, and Vawtrak,
Domain
- Plogesuct[.]com
- Cationfrob[.]ru
- Scientemplud[.]ru
- Orialoussin[.]ru
- Conaboory[.]ru
- Iderfeirel[.]com
- Lpertion[.]com
URI
- /4/forum.php
- /8/forum.php
10. Kovter
Kovter is a fileless click fraud malware and a downloader that evades detection by hiding in registry keys. Reporting indicates that Kovter can have backdoor capabilities and uses hooks within certain APIs for persistence.
![]()